Periapical x-rays Bitewing X-Rays 3D Cone Beam CT Scan Occlusal x-rays Panoramic x-ray Fluoride Therapy GC Tooth Mousse MI Paste Plus Fissure Sealing Scaling and Polishing Dental Fillings Composite and Amalgam Pulp Testing Extractions Hopeless Teeth Dental Sensitivity Oral Cancer Screening Dental Emergencies. Preparing a Patient for the Paralleling Technique.
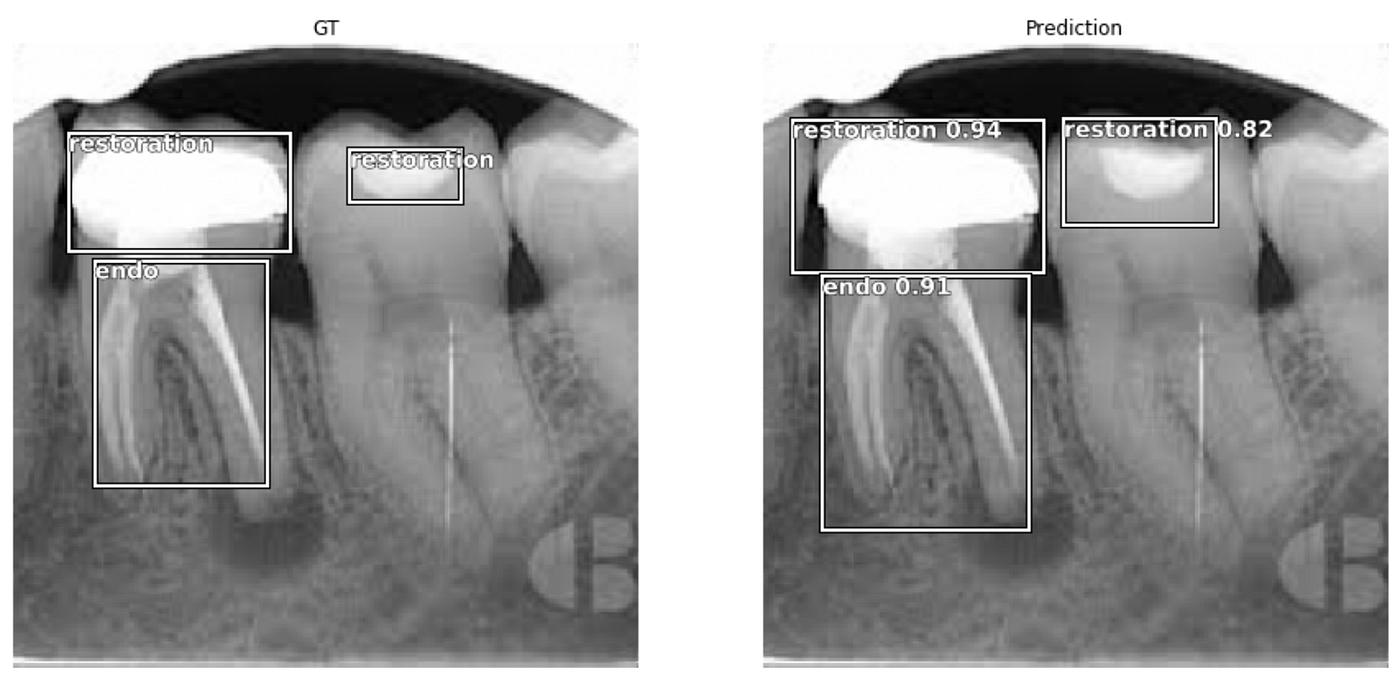
Fastai Object Detection Applied To Dental Periapical X Rays By John Persson Analytics Vidhya Medium
Different techniques and instruments are used to drain and decompress large periapical lesions ranging from placing a stainless steel tube into the root canal exhibiting persistent apical exudation 202 204 which is non-surgical decompression to placing polyvinyl or polyethylene tubes through the alveolar mucosa covering the apical lesion which is surgical.
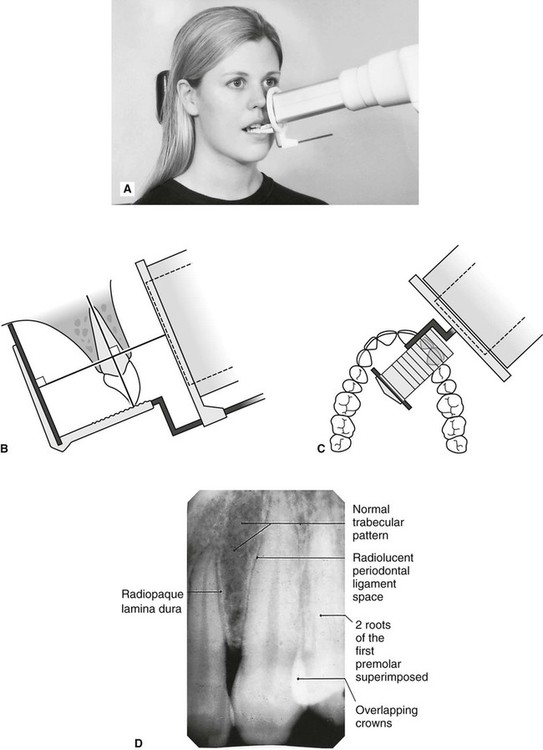
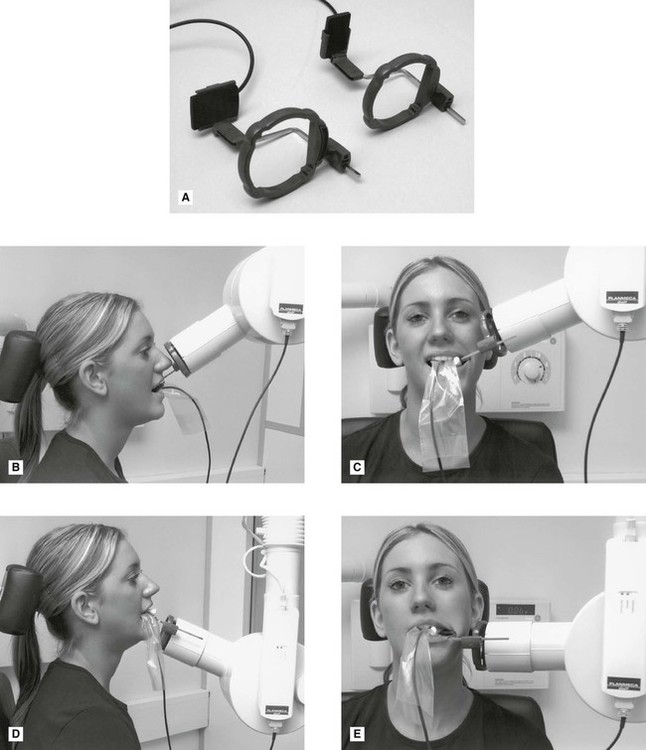
. By using a film sensor holder with still. Periapical views are used to record the crowns roots and surrounding bone. The snap-a-ray is used.
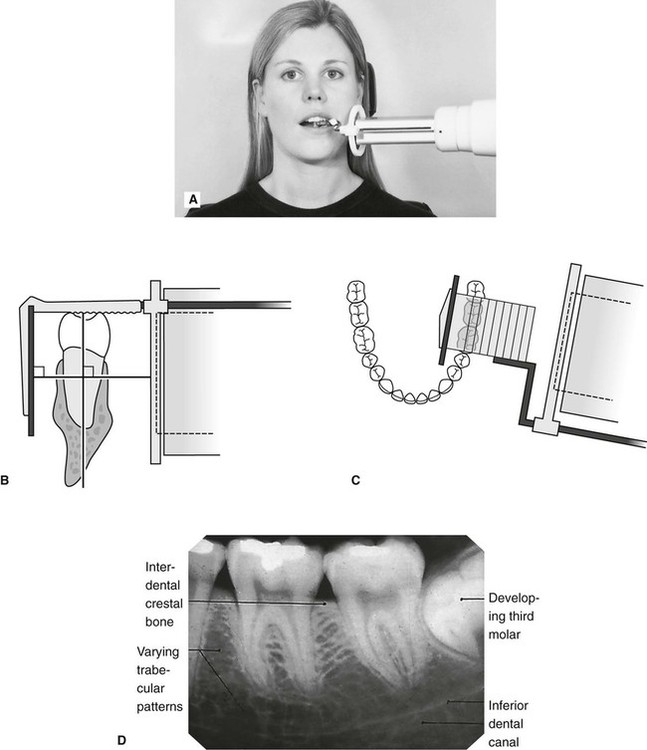
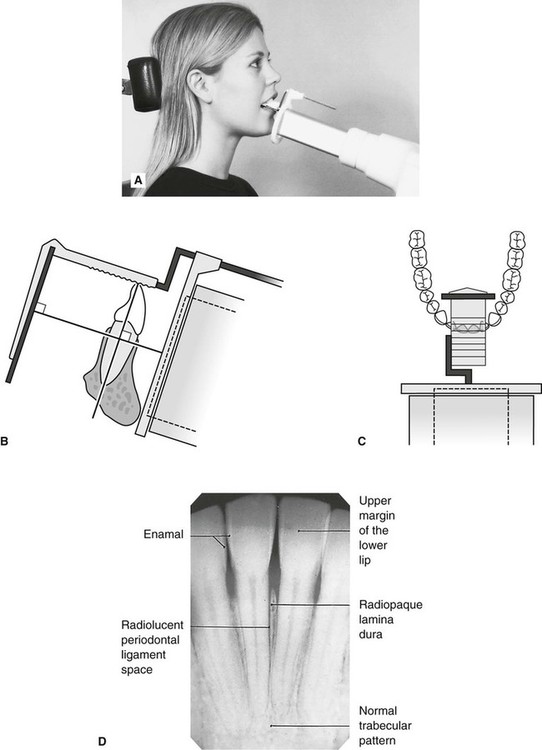
The X-ray tubehead is then aimed at right angles vertically and horizontally to both the tooth and the image. The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays. Periapical radiography is a commonly used intraoral imaging technique in radiology and may be a component of your radiologic examination.
Since the slope and curvature of the dental arches and the alveolar processes will not permit the film to be held close to the teeth. The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth to be radiographed and the central beam of X-ray is directed at right angle to the film and the teeth. The patient was positioned upright with hisher mouth was opened as wide as possible to allow the X-ray beam to pass to the sensor unobstructed from the opposite side of the mouth.
The sensor was placed. The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays. Periapical X-ray images expor ting results and reading results.
The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays. Instruction is provided in the use of dent hammers dent balls and barrels mandrels burnishers and other tools of the industry. The bisecting short-cone and paralleling long-cone techniques are two of the most commonly used techniques.
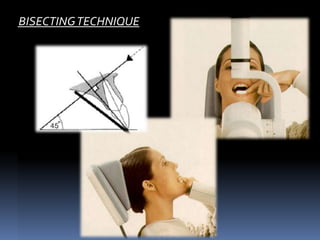
Changes to the angulation of the X-ray beam in relation to the teeth and film can help diagnosis and treatment by producing images which provide additional information not alway. Demonstration on how to take periapical x-ray using bisecting angle technique. The extraoral periapical radiographic technique was performed for both maxillary and mandibular teeth using Newman and Friedman technique2.
The paralleling technique is considered to be the best way to take periapical X-rays and when used correctly it should produce reliable images with minimal distortion. The image receptor is placed in a holder and positioned in the mouth parallel to the long axis of the tooth under. Parallel technique The image receptor is placed in a holder and placed in the mouth parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tooth under.
The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth in question and the central x-ray beam should be directed perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. To take a periapical exposure the hygienist or x-ray technician places a small photosensitive imaging plate coated with phosphorus into a sterile wrapper and inserts it into the patients mouth just like a conventional X-ray film card. The X-ray head is directed at right angles vertically and horizontally of both the tooth and the image receptor.
The central ray is directed to pass at a perpendicular angle to both the tooth and the film. The X-ray is taken and the exposed plate is then loaded into a scanner or processor which reads the image. I Periapical X-ray corroborates the periodontal regeneration in close contact with MTA filling.
Periapical radiographic techniques during endodontic diagnosis and treatment Int Endod J. Click to see full answer. Machine learning techniques th e more images in the dataset we.
For this purpose a special technique of periapical radiography was developed by Gordon M. Most frequently used radiography is for the periapical which is performed by the bisecting Thus when considering the execution of the radiographic technique and the possibility of errors that occur during the exposure of X-ray image XR receptors it is important to identify those that occur more frequently. The Bisecting Angle Technique is an alternative to the paralleling technique for taking periapical films.
Periapical film is held parallel to the long axis of the tooth using film-holding instruments. Periapical film is held parallel to the long axis of the tooth using film-holding instruments. The accelerated x-rays are decelerated by the target material resulting in bremsstrahlung.
The paralleling technique is recommended for routine periapical radiography but there are. A long cone is used to take x-rays with paralleling exposure techniques. By using a filmsensor holder with fixed image receptor and.
When comparing the two periapical techniques the. The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays. Single periapical radiographs are often made of individual teeth or groups of teeth to obtain information for treatment or diagnosis of localized diseases or abnormalities.
The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth in question and the central x-ray beam should be directed perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. DENTAL X-RAYS X-rays are produced by boiling off electrons from a filament the cathodeand accelerating the el to the target at the anode. X ray films hmdali.
Fitzgerald called as paralleling or long cone technique. Periapical radiographs provide important information about the teeth and surrounding bone. The film is placed parallel to the long axis.
Both techniques have advantages and disadvantages.
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry

Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
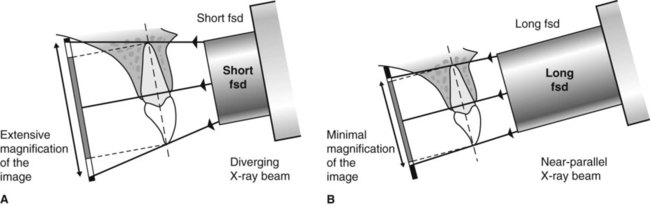
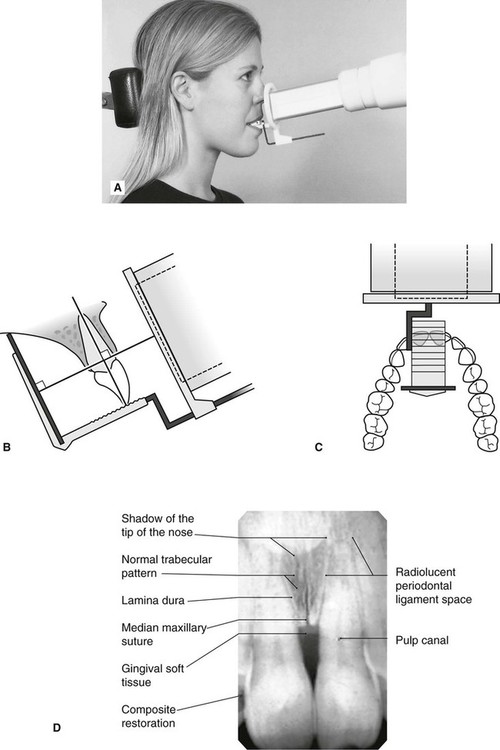
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry

0 comments
Post a Comment